Chronic FPIES, or Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome, is a challenging condition that requires careful management, especially when it comes to nutrition. This article explores effective nutritional strategies to help manage symptoms like chronic vomiting and weight loss, offering insights and personal experiences to guide you.
Chronic FPIES is a type of food allergy that primarily affects the gastrointestinal system. Unlike immediate allergic reactions, FPIES symptoms can take hours to appear and often include severe vomiting, diarrhea, and in some cases, lethargy and pallor. Chronic FPIES refers to ongoing symptoms that can lead to weight loss and nutritional deficiencies if not managed properly.

Managing Chronic FPIES involves navigating a complex landscape of dietary restrictions. Common trigger foods include rice, oats, dairy, and soy, but triggers can vary widely between individuals. Chronic vomiting can lead to dehydration and nutrient loss, while weight loss is a significant concern, especially in children.

Creating a personalized nutritional plan is crucial for managing Chronic FPIES. This often involves an elimination diet, where potential trigger foods are removed from the diet and then gradually reintroduced to identify specific triggers. Working with a healthcare professional, such as a dietitian or allergist, is essential to ensure the diet remains balanced and nutritionally adequate.
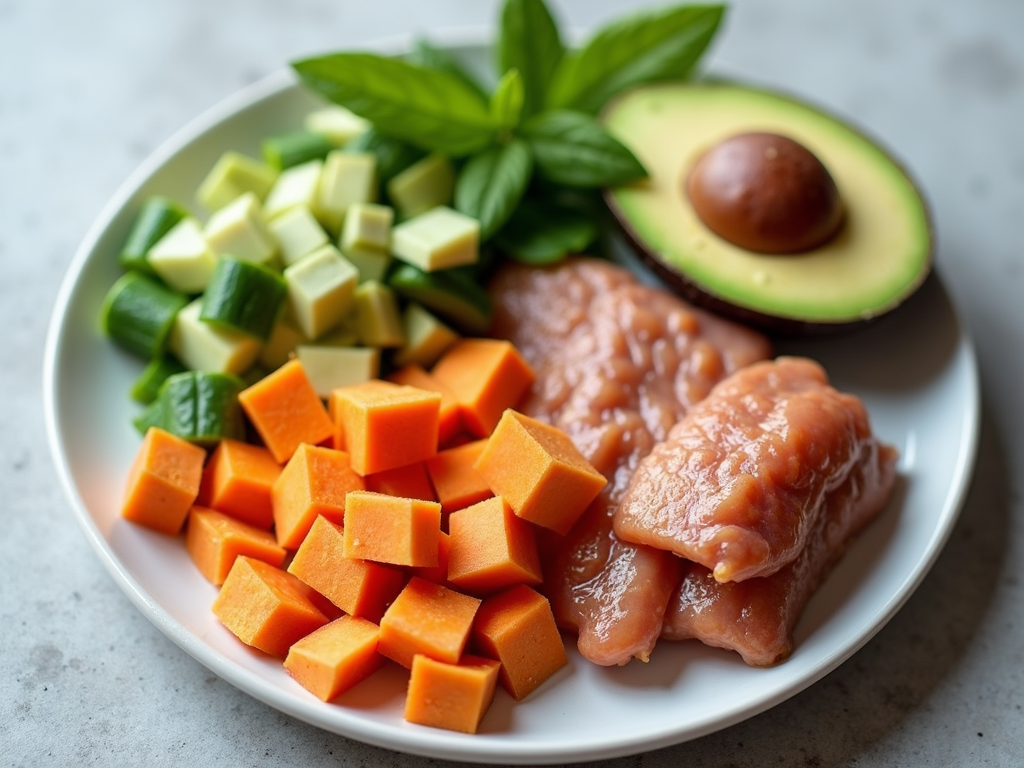
To combat chronic vomiting, it's important to focus on small, frequent meals that are easy to digest. Nutrient-dense foods, such as sweet potatoes, avocados, and lean proteins, can help maintain weight and provide essential vitamins and minerals. Hydration is also key, so incorporating electrolyte-rich fluids can be beneficial.

Living with Chronic FPIES can be daunting, but many families find ways to adapt and thrive. One parent shared, "It was tough at first, but once we identified the trigger foods and adjusted our diet, we saw a huge improvement in our child's health and energy levels." Sharing meals as a family, even with dietary restrictions, can help maintain a sense of normalcy.

Nutritionists emphasize the importance of a varied diet, even within the constraints of FPIES. "It's crucial to introduce new foods slowly and monitor for any reactions," says Dr. Jane Smith, a pediatric gastroenterologist. "Also, don't hesitate to seek support from dietitians who can help tailor a plan to your child's needs."

Managing Chronic FPIES requires a thoughtful approach to nutrition, focusing on identifying triggers, maintaining a balanced diet, and addressing symptoms like chronic vomiting and weight loss. By following these strategies and seeking professional guidance, individuals and families can improve their quality of life.
Discuss Here